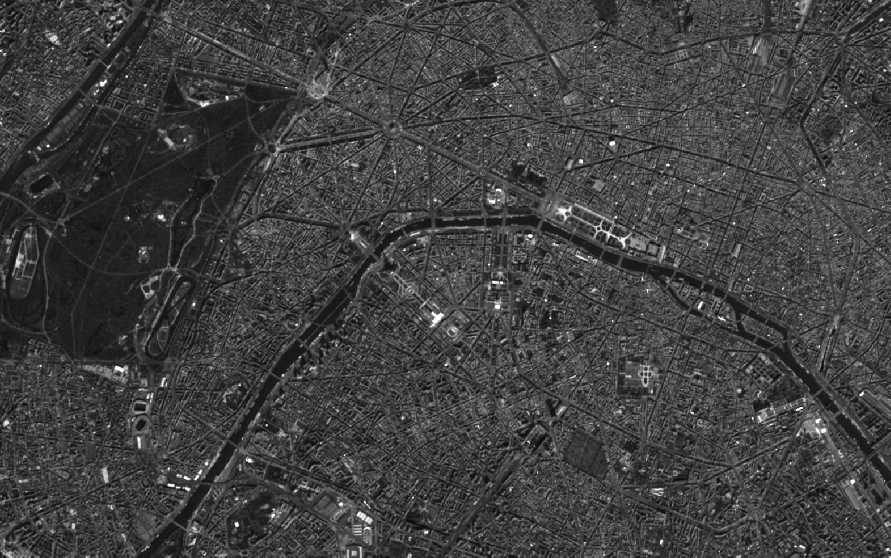
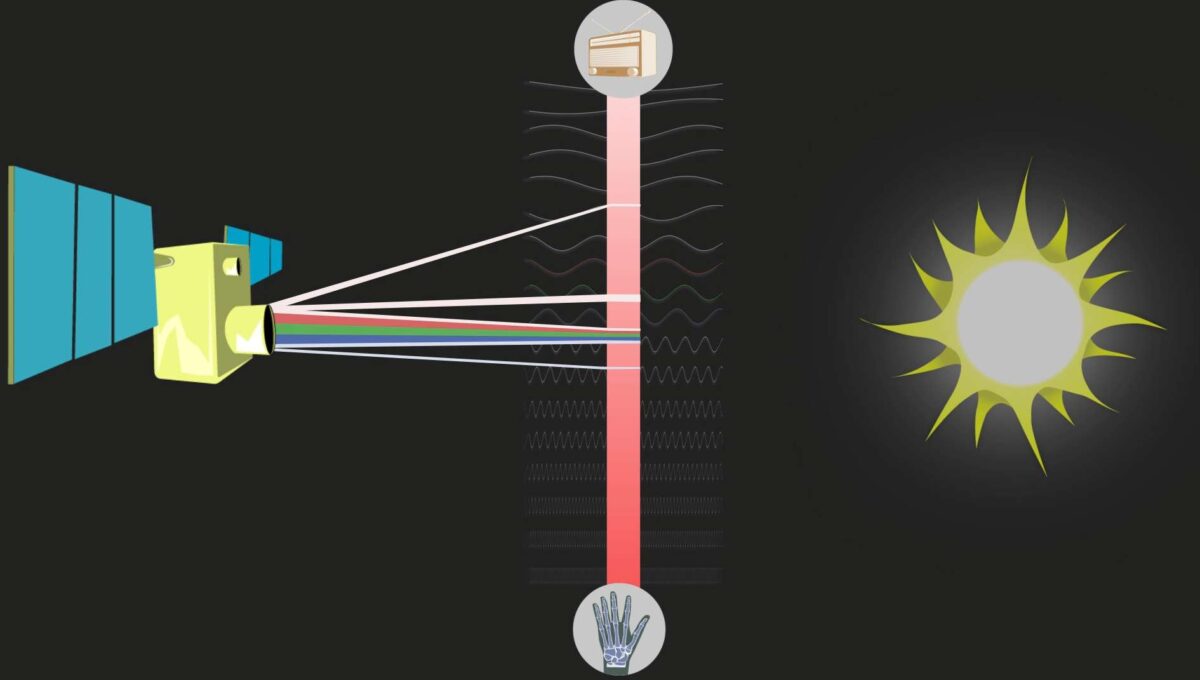
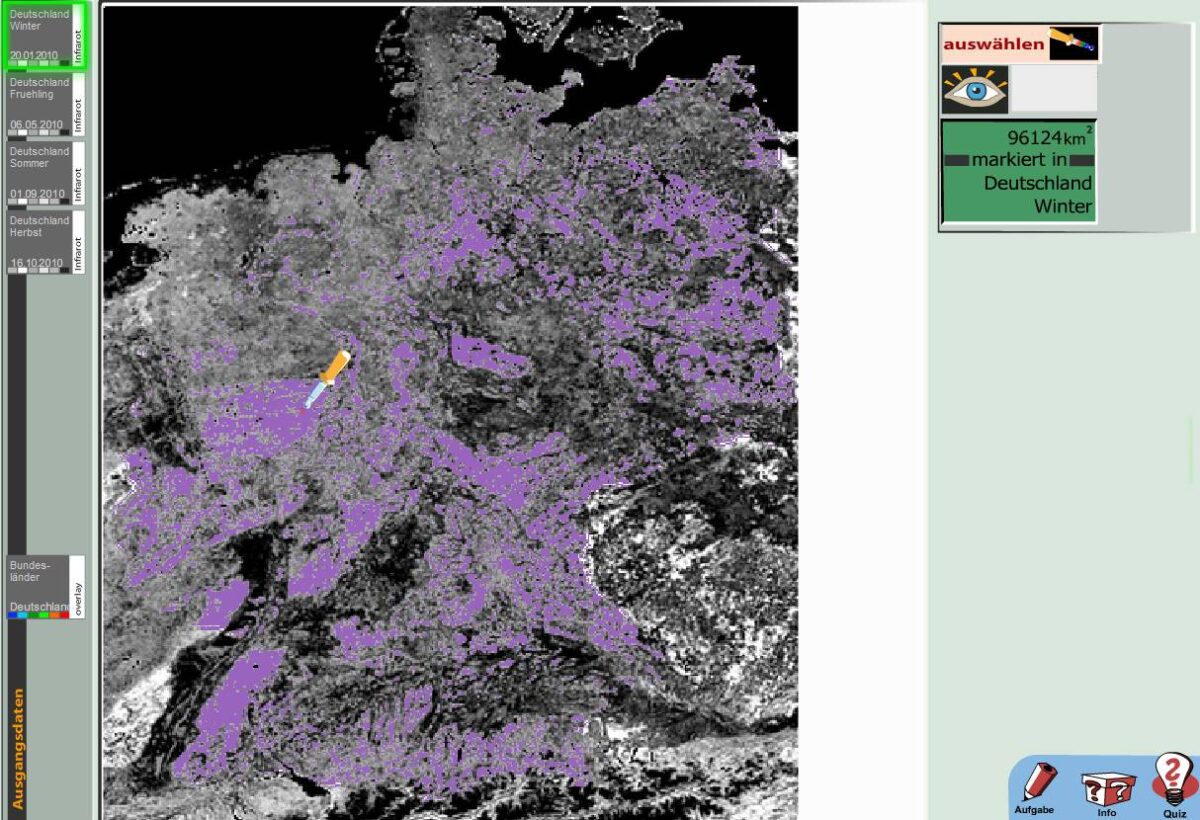
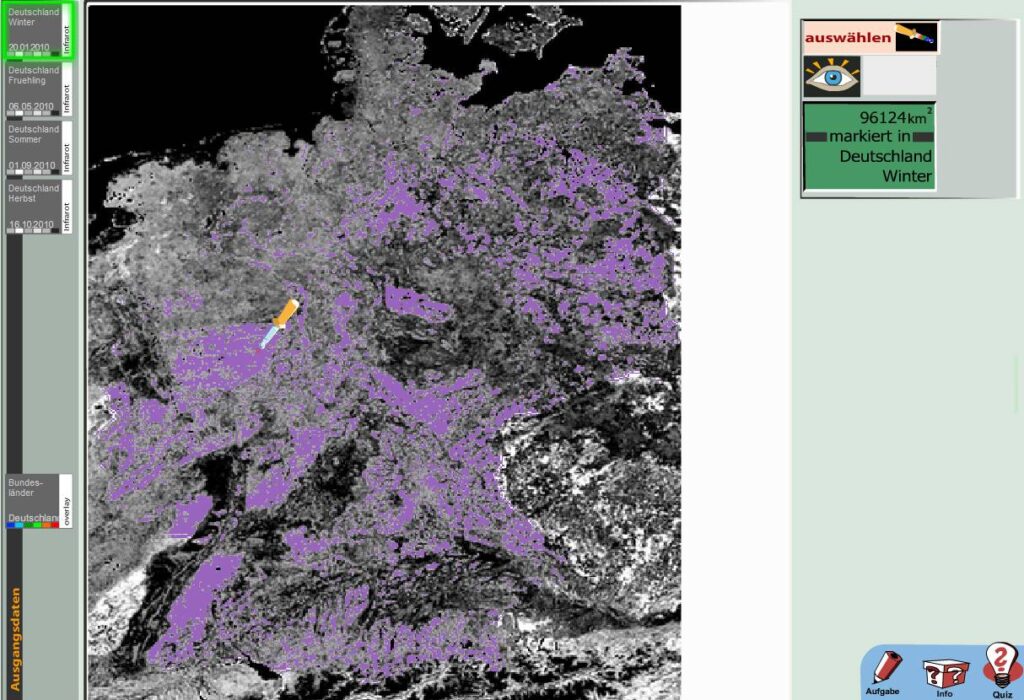
Mikrowellen sind nicht nur praktische viereckige Geräte auf dem Küchenschrank, die das Mittagessen von gestern aufwärmen, sondern sie sind auch wertvolle Informationslieferanten für die Erdbeobachtung. Gemeint sind aber natürlich nur die namensgebenden elektromagnetischen Wellen. Radarsatelliten senden langwellige Mikrowellenimpulse vom Weltall aus auf die Erde und empfangen die von Objekten reflektierten Mikrowellen. Aber wie wird dieses Echo am Ende eigentlich zu einem Bild? Und überhaupt: Ein Blick auf das elektromagnetische Spektrum zeigt uns: Wichtige Eigenschaften wie Farben, Temperaturen oder Pflanzenaktivitäten sind im Mikrowellenbereich gar nicht messbar. Also was messen Radarsensoren überhaupt?